Tag: H.264

A Proposed Hardware Reference Model for Spatial Transformation and Quantization in H.264,
This paper presents three Very Large Scale Integration prototypes to exploit spatial redundancy in the H.264 standard. The proposed architectures are: (1) forward 4 × 4 integer approximation of DCT transform and quantization, which is applied to all blocks of a frame, (2) the 4 × 4 Hadamard transform and quantization that is applied to the DC coefficients of the luma component when the macroblock is encoded in 16 × 16 intra prediction mode, and (3) the 2 × 2 Hadamard transform and quantization that is applied to the DC coefficients of the chroma component as a second level in the transformation hierarchy. The developed algorithms are adopted by the H.264 standard. A performance analysis shows that the architectures satisfy the real-time constraints required by different digital video applications.
I. Amer, W. Badawy, G. Jullien, “A Proposed Hardware Reference Model for Spatial Transformation and Quantization in H.264,” Elsevier Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, Volume 17, Issue 2, April 2006, Pages 533-552.
A Simplified 8×8 Transformation And Quantization Real-Time Ip-Block For Mpeg-4 H.264/Avc Applications: A New Design Flow Approach
Abstract
Current multimedia design processes suffer from the excessively large time spent on testing new IP-blocks with references based on large video encoders specifications (usually several thousands lines of code). The appropriate testing of a single IP-block may require the conversion of the overall encoder from software to hardware, which is difficult to complete in the short time required by the competition-driven reduced time-to-market demanded for the adoption of a new video coding standard. This paper presents a new design flow to accelerate the conformance testing of an IP-block using the H.264/AVC software reference model. An example block of the simplified 8 × 8 transformation and quantization, which is adopted in FRExt, is provided as a case study demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach.
Ihab Amer, Wael Badawy, Graham Jullien, Marco Mattavelli, And Robert Turney, “A Simplified 8×8 Transformation And Quantization Real-Time Ip-Block For Mpeg-4 H.264/Avc Applications: A New Design Flow Approach,” Journal of Circuits, Systems, and Computers Vol. 16, No. 6 (2007) 1011–1026
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications
Towards an H.264/AVC HW/SW Integrated Solution: An Efficient VBSME Architecture
Abstract:
This paper presents an efficient real-time variable block size motion estimation architecture. The proposed architecture provides motion vectors for each 16 times 16 block and its 40 sub-blocks. The proposed architecture is a single-instruction multiple-data architecture integrated with embedded SRAMs on one chip. The architecture has been prototyped using Xilinx Virtex-4 XC4VSX35-10 field-programmable gate array. It processes 30-CIF fps using 71-MHz clock frequency. Its maximum clock frequencyuency is 187.7 MHz and the maximum throughput is 20 4CIF fps. The prototyped architecture has 175 k gates and 18 kbits embedded SRAM.
Published in:
Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, IEEE Transactions on (Volume:55 , Issue: 9 )
- Page(s):
- 912 – 916
- ISSN :
- 1549-7747
- INSPEC Accession Number:
- 10185530
- DOI:
- 10.1109/TCSII.2008.923398
- Date of Publication :
- 23 May 2008
- Date of Current Version :
- 29 August 2008
- Issue Date :
- Sept. 2008
- Sponsored by :
- IEEE Circuits and Systems Society
- Publisher:
- IEEE
Mohammed Sayed, Wael Badawy, and Graham Jullien, “Towards an H.264/AVC HW/SW Integrated Solution: An Efficient VBSME Architecture”, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, Volume: 55, Issue: 9, pp. 912-916, Sept. 2008.
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications
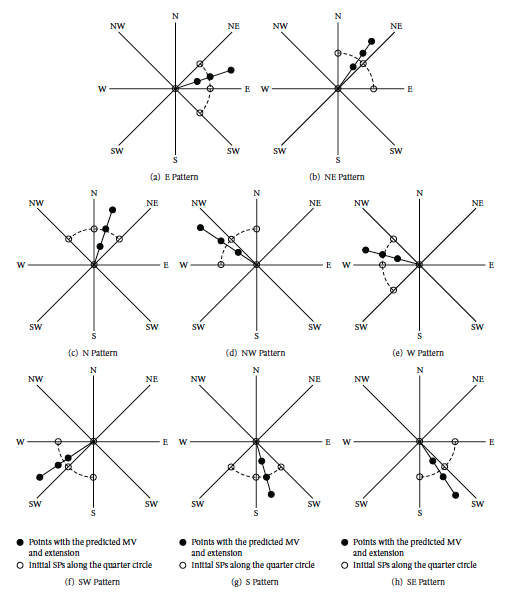
A Prototyping Virtual Socket System-On-Platform Architecture with a Novel ACQPPS Motion Estimator for H.264 Video Encoding Applications
Abstract
H.264 delivers the streaming video in high quality for various applications. The coding tools involved in H.264, however, make its video codec implementation very complicated, raising the need for algorithm optimization, and hardware acceleration. In this paper, a novel adaptive crossed quarter polar pattern search (ACQPPS) algorithm is proposed to realize an enhanced inter prediction for H.264. Moreover, an efficient prototyping system-on-platform architecture is also presented, which can be utilized for a realization of H.264 baseline profile encoder with the support of integrated ACQPPS motion estimator and related video IP accelerators. The implementation results show that ACQPPS motion estimator can achieve very high estimated image quality comparable to that from the full search method, in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), while keeping the complexity at an extremely low level. With the integrated IP accelerators and optimized techniques, the proposed system-on-platform architecture sufficiently supports the H.264 real-time encoding with the low cost.
Yifeng Qiu and Wael Badawy, “A Prototyping Virtual Socket System-On-Platform Architecture with a Novel ACQPPS Motion Estimator for H.264 Video Encoding Applications” EURASIP Journal on Embedded Systems, Volume 2009
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications
