Category: Journal Papers
A Computational Memory Architecture for MPEG-4 Applications with Mobile Devices
This paper presents a Computational Memory architecture for MPEG-4 applications with mobile devices. The proposed architecture is used for real-time block-based motion estimation, which is the most computational intensive task in the video encoder. It uses the exhaustive block-matching algorithm (EBMA) for motion estimation. The proposed architecture consists of embedded SRAMs and a number of block-matching units working in parallel to process video data while stored in the memory. The block-matching units access the embedded SRAMs simultaneously, which increases the speed of the architecture.
The architecture processes CIF format video sequences (i.e., the frame size is 352 × 288 pixels) with block size of 16 × 16 pixels and ±15 pixels search range. The proposed architecture has been designed, prototyped, and simulated for 0.18 μm TSMC CMOS technology. The simulation shows that the proposed architectures processes up to 126 CIF frames per second with clock frequency 100 MHz. The synthesized prototype of the proposed architecture includes 200 KB memory and it has an area of 33.75 mm2 and consumes 986.96 mW @100 MHz.
Mohammed Sayed , Wael Badawy, “A Computational Memory Architecture for MPEG-4 Applications with Mobile Devices,” Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for Signal, Image and Video Technology – Special Issue on Digital and Computational Video , Vol. 42, No. 1, pp. 35-42, January 2006.

A New Topology for a Current-mode Wheatstone Bridge
This paper presents a new topology for a current-mode Wheatstone bridge (CMWB) that uses an operational floating current conveyor (OFCC) as a basic building block. The proposed CMWB has been analyzed, simulated, implemented, and experimentally tested. The experimental results verify that the proposed CMWB outperforms existing CMWBs in terms of accuracy. A new CMWB linearization technique based on OFCC has been proposed, used, analyzed, and tested. The advantages of the proposed CMWB are fourfold. Firstly, it reduces the number of sensing passive elements; i.e., we can use two resistors instead of four and get the same performance as the traditional voltage-mode implementation. Secondly, we can apply the superposition principle without adding signal conditioning circuitry; therefore, the addition of sensor effects is possible. Thirdly, it has a higher common-mode cancellation. Finally, the proposed CMWB topology offers a significant improvement in accuracy compared to other CMWBs
Published in:
Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, IEEE Transactions on (Volume:53 , Issue: 1 )
- Page(s):
- 18 – 22
- ISSN :
- 1549-7747
- INSPEC Accession Number:
- 8954914
- DOI:
- 10.1109/TCSII.2005.854589
- Date of Publication :
- Jan. 2006
- Date of Current Version :
- 16 January 2006
- Issue Date :
- Jan. 2006
- Sponsored by :
- IEEE Circuits and Systems Society
- Publisher:
- IEEE
Yehya H. Ghallab, and Wael Badawy ” A New Topology for a Current-mode Wheatstone Bridge” IEEE Transaction on Circuit and System II, Volume 53, No.1, pp. 18-22, January 2006.
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications

DeFET: A Novel CMOS Electric-Field Sensor for Lab-on-a-Chip and Biomedical Applications
This paper presents a novel CMOS electric-field sensor, it is called the “differential electric-field sensitive field-effect transistor” (DeFET), which is based on a standard 0.18-mum Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) CMOS technology. The DeFET shows a sensitivity of 51.7 mV/(V/mum). This paper also describes the DeFET’s theory of operation in addition to the experimental and simulation results that confirm the DeFET’s theory of operation. Some applications of the DeFET in the area of lab on a chip and biomedical are also presented
Published in:
Sensors Journal, IEEE (Volume:6 , Issue: 4 )
- Page(s):
- 1027 – 1037
- ISSN :
- 1530-437X
- INSPEC Accession Number:
- 9008434
- DOI:
- 10.1109/JSEN.2006.877806
- Date of Publication :
- Aug. 2006
- Date of Current Version :
- 24 July 2006
- Issue Date :
- Aug. 2006
- Sponsored by :
- IEEE Sensors Council
- Publisher:
- IEEE
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications
Yehya Ghallab, Wael Badawy, “DeFET: A Novel CMOS Electric-Field Sensor for Lab-on-a-Chip and Biomedical Applications,” IEEE Sensors Journal, Volume 6, Issue: 4, Aug. 2006, pp. 1027 – 1037.

The Operational Floating Current Conveyor and Its Application
A five-port general-purpose analog building block, termed as an Operational Floating Current Conveyor (OFCC), is described. The OFCC combines the features of current feedback operational amplifier, second-generation current conveyor and operational floating conveyor. An implementation scheme of the OFCC is described and its terminal operational characteristics are used to yield a working device. The OFCC is then used as a single block to realize the current conveyors (CCII+ and CCII-) as well as the four basic amplifiers (i.e., voltage, current, transconductance, and transresistance amplifiers). The applications of the OFCC are presented and discussed. In the field of the analog filter synthesis, we proposed a new active universal second order filter using OFCC. It has three inputs and one output employing two OFCC, two capacitors and three resistors and can realize lowpass, bandpass, highpass, notch, and all pass filters from the same configuration. The proposed universal filters offer the following advantageous features: using active elements for the same type (OFCC). No requirement for component matching or cancellation constraints, which makes the filter easier to design, orthogonal adjustment of ω0 and Q and the circuits have low sensitivity. The simulation and experimental results are obtained and discussed.
Read More: https://www.worldscientific.com/doi/abs/10.1142/S0218126606003118
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications
Yehya Ghallab, Wael Badawy, M. Abo El-Ella, and M. Elsaid, “The Operational Floating Current Conveyor and Its Application“, Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers, Volume 15, No. 3, June 2006, pp. 351–372.
A Simplified 8×8 Transformation And Quantization Real-Time Ip-Block For Mpeg-4 H.264/Avc Applications: A New Design Flow Approach
Abstract
Current multimedia design processes suffer from the excessively large time spent on testing new IP-blocks with references based on large video encoders specifications (usually several thousands lines of code). The appropriate testing of a single IP-block may require the conversion of the overall encoder from software to hardware, which is difficult to complete in the short time required by the competition-driven reduced time-to-market demanded for the adoption of a new video coding standard. This paper presents a new design flow to accelerate the conformance testing of an IP-block using the H.264/AVC software reference model. An example block of the simplified 8 × 8 transformation and quantization, which is adopted in FRExt, is provided as a case study demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach.
Ihab Amer, Wael Badawy, Graham Jullien, Marco Mattavelli, And Robert Turney, “A Simplified 8×8 Transformation And Quantization Real-Time Ip-Block For Mpeg-4 H.264/Avc Applications: A New Design Flow Approach,” Journal of Circuits, Systems, and Computers Vol. 16, No. 6 (2007) 1011–1026
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications
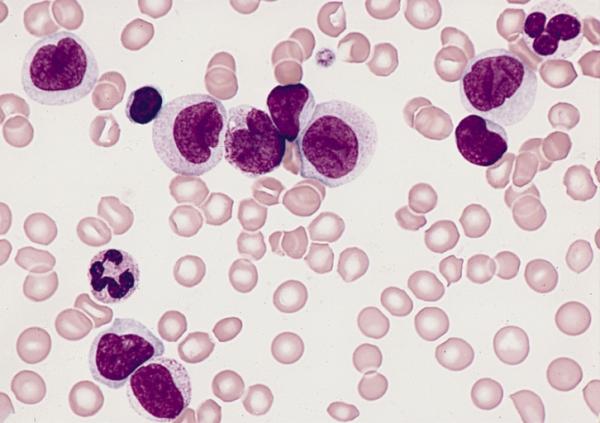
High-Throughput Identification and Classification Algorithm for Leukemia Population Statistics
Abstract:
Early detection of leukemia and reduced risk to human health can result from interdisciplinary integration of image analysis with clinical experimental results. Image analysis relies on efficient and reliable processing algorithms to make quantitative judgments on image data. This article presents the design and implementation of an efficient and high-throughput leukemia cell count and cluster classification algorithm to automatically quantify leukemia population statistics in the field of view. The algorithm is divided into two stages: (1) the cell identification stage and (2) the cell classification and inspection stage. The cell identification stage accurately segments background and noise from foreground pixels. A boundary box is generated enclosing the foreground pixels identifying all isolated cells and cell clusters. The cell classification and inspection stage uses one-dimensional intensity profiles that behave as signature plots to segregate isolated cells from cell clusters and evaluate total count within each cluster. The designed algorithm is tested with a variety of leukemia cell images that vary in image acquisition conditions, image sizes, cell sizes, intensity distributions, and image quality. The proposed algorithm demonstrates good potential in processing both ideal and nonideal images with an average accuracy of 91% and average processing time of 3 s. The performance of the proposed algorithm in comparison to recently published algorithms and commercial image analysis tool further ascertains its robustness.
Brinda Prasad and Wael Badawy, “High-Throughput Identification and Classification Algorithm for Leukemia Population Statistics,” The Journal of Imaging Science and Technology 52(3), 2008.
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications

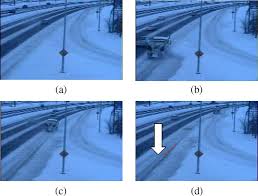
A Robust Video-Based Algorithm for Detecting Snow Movement in Traffic Scenes
Abstract
Video-based Automatic Incident Detection (AID) systems are widely deployed in many cities for detecting traffic incidents to provide smoother, safer and congestion free traffic flow. However, the accuracy of an AID system operating in an outdoor environment suffers from high false alarm rates due to environmental factors. These factors include snow movement, static shadow and static glare on the roads. In this paper, a robust real-time algorithm is proposed to detect snow movement in video streams to improve the rate of detection. This is done by having the AID system reducing its sensitivity in the areas that have snow movements. The feasibility of the proposed algorithm has been evaluated using traffic videos captured from several cameras at the City of Calgary.
Jun Cai, Mohamed Shehata, Wael Badawy, “A Robust Video-Based Algorithm for Detecting Snow Movement in Traffic Scenes”, The Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems for Signal, Image, and Video Technology, Special Issue on Signal Processing Systems, Volume 56, Numbers 2-3 / September, 2009, pp. 307-326.
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications
Towards an H.264/AVC HW/SW Integrated Solution: An Efficient VBSME Architecture
Abstract:
This paper presents an efficient real-time variable block size motion estimation architecture. The proposed architecture provides motion vectors for each 16 times 16 block and its 40 sub-blocks. The proposed architecture is a single-instruction multiple-data architecture integrated with embedded SRAMs on one chip. The architecture has been prototyped using Xilinx Virtex-4 XC4VSX35-10 field-programmable gate array. It processes 30-CIF fps using 71-MHz clock frequency. Its maximum clock frequencyuency is 187.7 MHz and the maximum throughput is 20 4CIF fps. The prototyped architecture has 175 k gates and 18 kbits embedded SRAM.
Published in:
Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, IEEE Transactions on (Volume:55 , Issue: 9 )
- Page(s):
- 912 – 916
- ISSN :
- 1549-7747
- INSPEC Accession Number:
- 10185530
- DOI:
- 10.1109/TCSII.2008.923398
- Date of Publication :
- 23 May 2008
- Date of Current Version :
- 29 August 2008
- Issue Date :
- Sept. 2008
- Sponsored by :
- IEEE Circuits and Systems Society
- Publisher:
- IEEE
Mohammed Sayed, Wael Badawy, and Graham Jullien, “Towards an H.264/AVC HW/SW Integrated Solution: An Efficient VBSME Architecture”, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II, Volume: 55, Issue: 9, pp. 912-916, Sept. 2008.
Link to the list of other Peer Journal Publications